 When speaking about IP convergence benefits, it is largely admitted that major benefits come from the fact that only one network has to be deployed and operated . When it comes to IP Telephony, then the attributes we retain are central deployment and administration, web based administration interface, mobility, openness in regard to all the voice and video applications that can be plugged on top. But what I will emphasise in this article is what VoIP and IP Telephony can bring to the application on top, and specifically to the Call Centre one.
When speaking about IP convergence benefits, it is largely admitted that major benefits come from the fact that only one network has to be deployed and operated . When it comes to IP Telephony, then the attributes we retain are central deployment and administration, web based administration interface, mobility, openness in regard to all the voice and video applications that can be plugged on top. But what I will emphasise in this article is what VoIP and IP Telephony can bring to the application on top, and specifically to the Call Centre one.
CISCO Call Centre Strategy
CISCO acquired GeoTel and WebLine in 1999, delivering a strong message to the market about its intention to be a leader in the contact centre market. GeoTel at that time was delivering a CTI middle-ware solution, namely the Intelligent Call Router that has become the Intelligent Contact Manager. Today a specific Business Unit in Cisco, the Customer Contact Business Unit, is focusing on 3 major missions:
1 Delivering to the market, a multi-channel contact center solution that integrates not only to CRM applications but also to platforms delivering e-services to the end user (e-commerce, e-support, e-seminar).
2 Providing our customers with a clear and ‘smooth’ migration path from TDM voice networks to VoIP and IP Telephony, from low and medium range solution with IPCC Express Edition to a high end solution with the IPCC Enterprise Edition, and from call centers to a Customer Interaction Networks.
3 Promoting technical partnership with third party vendors, including CRM vendors such as Siebel, SAP, Oracle, People Soft, and E.piphany.
CISCO Intelligent Contact Management (ICM)
ICM provides carrier-level or enterprise-level network pre-routing or post-routing of customer contacts, based on agent skills and availability. ICM is pre-integrated with various types of call centre equipment and solutions from a plethora of third party vendors.
Pre-integration is realised thru connectors taking advantage of CISCOs opened, standards-based CTI interface. These solutions include ACDs, dialers, IVRs, recorders, CRM applications, and wall boards, and cover the full spectrum of contact center applications.
The ICM Administration Workstation provides a user-friendly and powerful GUI (Graphic User Interface), to administer, monitor and control ACD (Automatic Call Distributor) and IVR (Interactive Voice Response) services from different vendors, located in multiple remote sites.
WebLine was delivering three solutions considered amongst the best of breed in the market to manage incoming email in a call centre environment and provide web based collaboration services for e-commerce, e-support and e-seminar applications.
These solutions have been packaged and renamed by CISCO inside the Customer Interaction Suite that includes CISCO Email Manager (CeM), CISCO web-Collaboration and also CISCO Media Blender delivering web call back and multi-mode collaboration services for agents behind a traditional TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) ACD.
With ICM 5.0, CeM and CCS (CISCO Collaborative Server) have been fully integrated with ICM, and will be no more sold as standalone solutions but rather as an option complementing the ICM offering.
IP Contact Centre Solutions – release 5.0
Cisco IPCC Enterprise Edition delivers intelligent contact routing, call treatment, network-to-desktop computer telephony integration (CTI), and multi-channel contact management over an IP infrastructure.
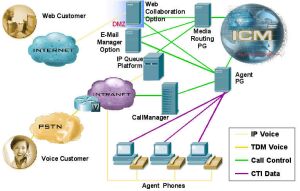 By combining multi-channel ACD functionality with IP telephony in a unified solution, IPCC Enterprise enables companies to rapidly deploy a distributed contact center infrastructure. IPCC Enterprise Edition also allows customers to leverage their investment in TDM technologies, by interoperating with TDM ACDs and IVRs.
By combining multi-channel ACD functionality with IP telephony in a unified solution, IPCC Enterprise enables companies to rapidly deploy a distributed contact center infrastructure. IPCC Enterprise Edition also allows customers to leverage their investment in TDM technologies, by interoperating with TDM ACDs and IVRs.
IPCC provides advanced supervision feature like call recording, call barge in, call intercept and silent monitoring, where the capability to remote agent is built in the system.
Furthermore IPCC Enterprise is part of Ciscos family of IP Communications solutions and is built on top of Cisco AVVID (Architecture for Voice, Video, and Integrated Data) that offers a full range of enterprise solutions for enhancing employee performance and enabling better communication. Solutions include Personal Assistant, Automatic Attendant, and Cisco Unity for Unified Communications.
Cisco also delivers IPCC Express Edition, which has been designed to meet the needs of the small to mid-market contact center, with integrated ACD, CTI, and IVR functionality delivered on a single platform. This solution can be migrated to the IPCC Enterprise Edition, with reuse of IVR functionality, including queuing, and preserving the CTI integration with other third party vendor applications and CRM.
Enterprises are also looking how they can extend their web services to voice services or vice versa. CISCO proposed several solutions to easy this migration process that focus on web and voice integration but also on VoiceXML, allowing multimodal interaction with the customer.
The Cisco Customer Response Solution has been designed has an opened workflow engine running the IVR service but also supporting the IPCC Express Edition logic specified in JavaBeanstm steps, part of the IVR service logic description.
The CRS service creation graphical user interface includes specific steps libraries to allow web and e-mail interaction with an external application and to connect relational database thru Microsoft Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) and Java Database Connectivity (JDBC). CRS supports advanced IVR features like Text To Speech, Automated Speech Recognition and VxML. This CRS workflow engine could be enriched with customized JavaBeanstm steps Library to interact with the own customer environment. Cisco voice enabled routers have support also for VxLM, a feature built in the Cisco Internet Operating System.
The business benefits of IP in the contact center
The business benefits of IP convergence generally extend to the applications running in the converged network environment, and bring the following advantages:
1 Total flexibility in deploying and dimensioning the system in either a centralized or distributed manner.
2 The important functions of the telephony system and call center systems have been split in separate components to be deployed in a very modular and flexible way. For instance queuing is done thru any TDM or IP IVR, either on the customer premises or hosted in the carrier network, so call can be queued as close as possible to the caller.
3 In a very similar way call control is realized by a cluster of Call Manager which controls in turn IP phones and VoIP Gateways distributed all over the enterprise or SP network. The switching matrix confined traditional to the ACD or PBX is now crossing even the enterprise boundary if a Voice VPN extends the enterprise network.
4 Contact Routing is done thru a unique and centralized component that can apply a set of strategies to route different media in a consistent way and provide consolidated statistics to contact center administrators and supervisors. IPCC Enterprise allows mixed incoming voice calls, outbound calls, e-mail, voice mails, faxes and web call back in a completely controlled and blended environment, and delivered to the agent desktop.
5 CTI interface to the agent and supervisor desktops along with other third party applications such as CRM, dialer, and WFM tools is done in a completely decentralized way thru a CTI Object Server (CTI OS) to be deployed on each remote location when needed. CTI OS supports the concept of an ultra light CTI client, greatly simplifying CTI deployment and bringing all the simplification of a web based interface.
6 Support for remote agent in such architecture is done natively without any hardware to be added or solution to be re-designed. Only consideration should be taken in case of WAN failure, where today only telephony features are preserved thanks to a new Survivable Remote Site Telephony feature built-in the router.
7 Low cost, low resource outbound call blending solution. Cisco IPCC Outbound Option enables contact centers to seamlessly blend inbound and outbound calls under IPCCs scripting control. This functionality extends over multiple sites, and is entirely software-based. No telephony hardware cards are required to enable the outbound dial; instead the Voice Gateway places and classifies all outbound calls.
Cisco offers a full solution set for contact centers but differentiates from competition that offers a point solution rather that an open communication and interaction platform. This architecture extend the concept of having different telephony servers from different vendors like IVR and ACD interacting together to a new concept of media server where the media is not only phone calls, but also includes web, e-mail, fax and voice mail.
Cisco paves the way to the next generation CTI integration where not only CRM, and back office application can integrate with Voice system, but also new media server that enrich considerably the way customer interacts with agent in an asynchronous or multi modal way (e.g. web call back with web collaboration, web form sharing and chat enable in the same session).
Customers also leverage Ciscos end-to-end vision, since it is critical that the solution has been designed from an end-to-end perspective in regard to QoS, but also security and routing. To illustrate this concept enterprises must consider the contact center solution running on top of a VoIP VPN network where dial plan, call admission, and security needs to be taken in to consideration all together from the VPN client up to agent IP phone and desktop.
The same applies to an ICM deployment across the WAN, where many enhancements have been made to ease the classification of ICM critical traffic to identify this traffic to account for QoS policy and attributes. Regarding security the Cisco Collaboration Server has been designed with best practices in mind, so the light Java applet running on the agent and caller browser only issue http request toward the CCS deployed in the DMZ area.
Beyond Call Centers and Toward a Customer Interaction Network
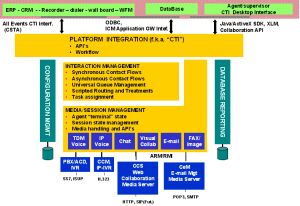 Two major interfaces, the Agent Reporting and Management (ARM) and the Media Routing Interface (MRI) permit the media server integration with ICM. The ARM and MRI interfaces are respectively designed to report the real time status of agents and contacts, and to forward routing request to the ICM, in charge of assigning an answering resource to that contact.
Two major interfaces, the Agent Reporting and Management (ARM) and the Media Routing Interface (MRI) permit the media server integration with ICM. The ARM and MRI interfaces are respectively designed to report the real time status of agents and contacts, and to forward routing request to the ICM, in charge of assigning an answering resource to that contact.
A media server can assign itself an agent to a contact, after the agent has been reserved by the ICM. This mechanism is implemented by CeM, so agent can handle e-mails in a pull mode rather than in a push mode.
Each Media Server gets the opportunity to analyse and handle the contact before routing, taking advantage of any specificity characterising this channel of communication.
For instance, CeM deeply analyses email in regard to their content, and header before any routing decision is taken based on that content analysis. Same for a web call back request, where a web form or the history of URL accessed by the customer can be used to enrich the contact information to be delivered to the routing engine, the CRM applications and finally displayed to the agent CTI desktop.
The media server will also handle the very specific way an agent can interact with a ‘caller’ depending on which media has been chosen. CeM after analysing the email is able to acknowledge the receipt of that email automatically, and format dynamically different templates to be used for the answer.
CCS displays a collaboration toolbar both on the agent and customer browsers to pilot the different collaboration phases where agent for instance can trigger follow-me mode, or simply retrieve on demand web pages and web forms from the customer, or conversely.
The communication channel influences also the way supervisor can intervene. Supervisors in CeM can apply a filter to a queue of emails, modify their priority and attributes, and move them from one queue to another. These features are referred as bulk management tools. Email can also be automatically escalated when they are overdue.
ICM implements the universal queue by routing contact to agent in respect to all media specificities. For instance ICM is able to push web paged when a web call back request is in queue. ICM can forward several simultaneous chat session to the same agent, or interrupt an email process if an incoming call is considered as taking precedence.
For multi-modal contact, like web call back with collaboration, the ICM CTI server will be in charge of synchronizing all the different sessions for each media, handling multi-session transfer from one agent to another agent.
So ICM implements not only a communication layer between agent and contacts, but it is also involved in synchronising different interactions at the agent desktop, particularly when multi-mode communication is involved.
To conclude, Cisco Customer Contact Software enables customers to move into the next phase of customer contact – beyond today’s Contact Center to a Customer Interaction Network. The Customer Interaction Network is a distributed, IP-based customer service infrastructure that comprises a continuously evolving suite of innovative, multi-channel services and customer relationship management applications.
These services and applications provide enhanced responsiveness and streamlined customer exchanges to help your organization deliver superior customer service. A Customer Interaction Network extends customer service capabilities across the entire organization, giving your business a more integrated and collaborative approach to customer satisfaction.
Philippe Perin (perinp@cisco.com)
2003-02-19
Em Foco – Opinião

