
All the IP convergence benefits are well known and can be summarised essentially in deploying and operating only one network. When it comes to IP Telephony, then the attributes we retain are central deployment and administration, web based administration interface, mobility, openness in regard to all the voice and video applications that can be plugged on top. But what I will emphasise in this article is what VoIP and IP Telephony can bring to the application on top, and specifically to the Call Centre one.
CISCO Call Centre Strategy
CISCO acquired Geotel and Webline in 1999, delivering a strong message to the market about its intention to be a leader in the contact centre market. Geotel at that time was delivering a CTI middle-ware solution, namely the Intelligent Call Router that becomes the Intelligent Contact Manager. CISCO has meanwhile created an autonomous Contact Centre Business Unit.
CISCO Intelligent Contact Management (ICM)
ICM provides inside the carrier or enterprise network pre or post-routing of call, based on skills and agent availability. ICM is pre-integrated with a lot of different call centre equipment and solutions from a plethor of third party vendors. Pre-integration is realised thru connectors taking advantage of CISCOs opened CTI interface.
The ICM Administration Workstation provides a convivial and powerful GUI (Graphic User Interface), to administer, monitor and control ACD (Automatic Call Distributor) and IVR (Interactive Voice Response) services from different vendors, located in multiple remote sites.
Webline was delivering three solutions considered amongst the best of breed in the market to manage incoming email in a call centre environment and provide web based collaboration services for e-commerce, e-support and e-seminar applications.
These solutions have been packaged and renamed by CISCO inside the Customer Interaction Suite that includes CISCO Email Manager (CeM), CISCO web-Collaboration and also CISCO Media Blender delivering web call back and multi-mode collaboration services for agents behind a traditional TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) ACD.
With ICM 5.0, CeM and CCS (CISCO Collaborative Server) have been fully integrated with ICM, and will be no more sold as standalone solutions but rather as an option complementing the ICM offering.
IP Contact Centre Solutions – release 5.0
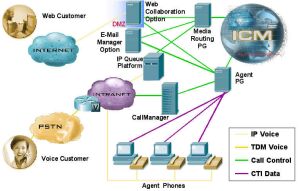 IP Contact Centre (IPCC) package combines ICM, CeM and CCS with Cisco Call Manager, to build a complete, IP based, solution for Call Centre. IPCC allows customers to connect to their traditional ACD and IVR legacy systems, while taking advantage of CISCO IP Telephony utility based on Cisco Call Manager solution.
IP Contact Centre (IPCC) package combines ICM, CeM and CCS with Cisco Call Manager, to build a complete, IP based, solution for Call Centre. IPCC allows customers to connect to their traditional ACD and IVR legacy systems, while taking advantage of CISCO IP Telephony utility based on Cisco Call Manager solution.
IPCC provides advanced supervision feature like call recording, call barge in, call intercept and silent monitoring, where the capability to remote agent is built in the system.
Furthermore IPCC is built on top of CISCO AVVID (Audio Video Voice Integrated Data) architecture that offers a full range of enterprise solutions for enhancing the employee performance and allow better communication, like Personal Assistance, Automatic Attendant and UNITY as the unified communication solution.
CISCO delivers also an IPCC Express Edition developed on top of the CRS (Customer Response Solutions) platform where focus has been made on packaging, and pricing to address the small and medium enterprise call centre business.
This solution can be very easily migrated to the full IPCC Enterprise Edition, re-using CRS capacity as a queue point and IVR platform, and preserving the CTI integration with other third party vendor application and CRM.
Enterprises are also looking how they can migrate their web services to voice services or vice versa. In the call centre area this is even truer since customer can contact and interact with agents thru the web.
CISCO proposed several solutions to easy this migration process that focus on web and voice integration but also on VoiceXML, allowing multimodal interaction with the customer.
The benefits of being IP
The benefits of the IP convergence can be rolled out to the application running on top, and bring the following advantages to it:
1 Total flexibility in deploying and dimensioning the system in a central or distributed way. The only criteria being retained are the WAN (Wide Area Network) bandwidth, the WAN availability and if it has been QoS (Quality of Service) enabled to allow VoIP toll by-pass.
2 The important functions of the telephony system and call centre systems have been split in separate components to be deployed in a very modular and flexible way. For instance queuing is done thru any TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) or IP IVR (Interactive Voice Response), this later being either customer premises based or hosted in the carrier network, so call can be queued as closed as possible to the caller.
3 In a very similar way call control is realised by a cluster of Call Manager which controls in turn IP phones and VoIP Gateways distributed all over the enterprise. The switching matrix confined traditionally to the ACD (Automatic Call Distributor) or PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is now crossing even the enterprise boundary if a Voice VPN (Virtual Private Network) extends the enterprise network.
4 Routing is done thru a unique and centralised component, the ICM, which can apply a set of strategies to route different media in a consistent way and provide consolidated statistics to the call centre administrator and supervisors. ICM will permit to mix incoming voice calls, outbound calls, email, voice mails, faxes and web call back in a completely controlled and blended way up to the agent desktop.
5 CTI interface to the agent and supervisor desktops along to any other third part applications like CRM, dialler, WFM (Workflow Management) tool is done thru a CTI Object Server to be deployed locally or centrally. CTI OS supports the concept of an ultra-light, web based, CTI client simplifying greatly the deployment and bringing all the simplification of a web-based interface.
6 Support for remote agent in such architecture is done natively without any hardware to be added or solution to be re-designed. Only consideration should be taken in case of WAN failure, where today only telephony features are preserved thanks to a new Survivable Remote Site Telephony feature built-in the router.
7 Finally the Outbound call solution from CISCO, namely the IPCC Blended Agent option allows to rollout the same outbound calls campaign over multiple sites and does not require any hardware devices to dial out, since the VoIP gateway is placing outbound call and classifying these calls on behalf of the ICM.
CISCO offers a full solution set for Call Centre but differentiates from competition that offers a point solution rather than an open communication and interaction platform. This architecture extends the concept of having different telephony servers from different vendors like IVR and ACD interacting together to a new concept of media server where the medium is not only phone calls, but also encompasses web, email, fax and voice mail.
CISCO paves the way to the next generation CTI integration where not only CRM, and back office application can integrate with voice system, but also with different media server solutions that enriches considerably the way customer interacts with agent, enabling multi-mode interaction (e.g. web call back with web collaboration, chat with web form sharing).
Why an open communication and interaction platform is necessary?
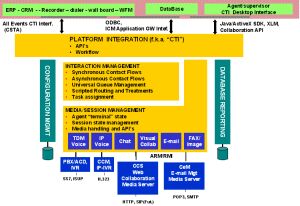 The same question could be asked differently: Why routing, and queuing should be a separate solution from contact handling and processing? This explanation below refers to the CISCO Contact Centre Open Communication and Interaction Platform that allow a horizontal integration layer rather than a vertical one.
The same question could be asked differently: Why routing, and queuing should be a separate solution from contact handling and processing? This explanation below refers to the CISCO Contact Centre Open Communication and Interaction Platform that allow a horizontal integration layer rather than a vertical one.
Three major interfaces, the Agent Reporting and Management (ARM), Message Routing Interface (MRI) and ConAPI permit the integration of CCS and CeM with ICM. These three interfaces are respectively designed to allow any system to report agent and contact status, forward routing request to ICM and allow different platforms to share configuration data on agents and skills.
The MRI allows also any external Media Server to select the agent after being reserved thru the ICM. This mechanism allows for instance the CeM agent desktop interface to work in a pull mode, where the agent is proposing a list of email and can pick up one, opposed to the push mode where the agent is imposed an email.
Each Media Server gets the opportunity to analyse and handle the contact before routing, taking advantage of any specificity characterising this channel of communication. For instance, CeM deeply analyses email in regard to their content, and header before any routing decision is taken based on that content analysis.
Same for a web call back request, where a web form or the history of URL accessed by the customer can be used to enrich the contact information to be delivered to the routing engine, the CRM applications and finally displayed to the agent CTI desktop.
The media server will also handle the very specific way an agent can interact with a ‘caller’ depending on which media has been chosen. CeM after analysing the email is able to acknowledge the receipt of that email automatically, and format dynamically different templates to be used for the answer.
CCS displays a Collaboration Toolbar both on the agent and customer browsers to pilot the different collaboration phases where agent for instance can trigger follow-me mode, or simply retrieve on demand web pages and web forms from the customer, or conversely.
The communication channel influences also the way supervisor can intervene. Supervisors in CeM can apply a filter to a queue of emails, modify their priority and attributes, and move them from one queue to another. These features are referred as bulk management tools. Email can also be automatically escalated when they are overdue.
ICM implements the universal queue by routing contact to agent in respect to all media specificities. For instance ICM is able to push web paged when a web call back request is in queue. ICM can forward several simultaneous chat session to the same agent, or interrupt an email process if an incoming call is considered as taking precedence.
For multi-modal contact, like web call back with collaboration, the ICM CTI server will be in charge of synchronizing all the different sessions for each media, handling multi-session transfer from one agent to another agent.
So ICM implements not only a communication layer between agent and contacts, but it is also involved in synchronising different interactions at the agent desktop, particularly when multi-mode communication is involved.
To conclude, the major benefit of an IP converged network comes from the fact that voice and video is processed in exactly the same way as other media like chat, email, and web collaboration. In a sense that now, these media can be controlled centrally or remotely thru IP-based protocols.
Em Foco – Opinião

